Quizlet What Are Parents Of Children Who Develop Learning Goals Likely To Do?
Edifice resilience in children is more than teaching children life skills. Let's notice out what resilience is, what the major resilience factors are and how the four science-backed tips can assist raise resilient children.
As parents, nosotros desire to protect our children from impairment.
But we know we can't shelter them from every single threat or challenge that may come their way, now or in the future.
And so we want our young children to be able to cope with stress and change – to bounce back from whatever life throws at them.
In short, we desire to enhance resilient children.
But how tin can we do that? The adept news is that researchers are finding that resilience isn't some elusive innate quality – it'south not a "yous've either got it or you don't" proffer.
Rather, it is something that's built and strengthened through specific life experiences.

What Is Resilience
Resilience is the process of handling dissimilar types of stress and recovering from trauma or arduousness in tough times.
From early life hardship or abuse to loss of a parent, fractured relationships, loss of a loved one, job loss, health problems, or natural disasters – trauma can come up in whatsoever number of packages. A resilient person can go on performance and fifty-fifty thrive later on.
Resilient individuals recover faster and more completely from adverse experience, and may even emerge relatively unscathed from astringent hardship.
Childhood psychology experts take long been fascinated by the fact that some children who've faced trauma tin come up out by and large unharmed, while others crumble. They wanted to know why.
For more help on calming tantrums, check out this footstep-by-stride guide


At first, researchers focused on identifying individual characteristics that are potential risks such every bit personality traits and vulnerabilities that could contribute to negative outcomes in children i . Just afterwards researchers turned this approach on its head: They started looking into factors that contributed to positive outcomes in at-risk children, instead 2 .
They call these factors "resilience factors" or "protective factors." These are the variables that, when present in a child's life, stand for to being more than resilient and better wellness outcomes. Not just that, but they also seem to add up: The more protective factors are present, the meliorate the chance a child tin adapt positively to difficult circumstances.
All the same, these risk factors tin add up, as well. Children exposed to six or more risk factors are 2.5 times more probable to develop externalizing disorders, such as comport disorder, vehement crime, and substance corruption. They are also 1.viii times more likely to develop internalizing disorders that affect children's mental health, such every bit depression and anxiety disorders two,three .
The concept of resilience is essentially the accumulation of protective factors vs. run a risk factors. Think of information technology like a scale: Stack the protective factors on 1 side and the risk factors on the other.
Children go resilient when the effect of the protective factors outweighs the adventure factors. This ways that children with a history of pregnant adversity may require a lot more positives to tip the scale and go resilient.
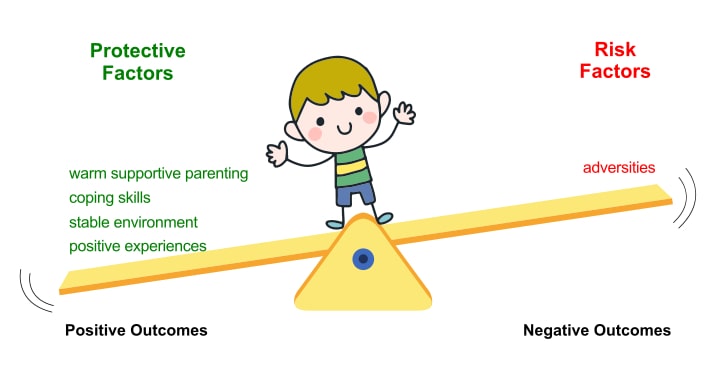
Resilience Factors That Can Aid Children Suit
So what are these protective factors that can assist children cope with hardship?
Researchers have identified numerous factors that they group into iii full general categories: family, individual, and customs. They bear upon various issues, just at that place'southward a recurrent theme that runs through many of these factors: connectedness with supportive people.
Indeed, six decades of inquiry indicate that a child'south resilience mostly depends on their connections to other people, rather than their ain inherent qualities 4 .
Examples of resilience factors that can help kids adapt v .
1. Family Factors:
- Good parenting.
- Depression family unit stress.
- Sound parental mental health.
- Absence of alcoholism, drug abuse, etc.
- Sense of rubber.
2. Individual Factors:
- Adaptive emotional skills.
- Perception of control and the child's ability to bear on one's own life.
- Cocky-esteem and self-efficacy.
- Ability to dream or having a sense of purpose in life.
- Social skills and communication skills.
- Empathy.
- Sense of humor.
- Physical health.
- College intellectual capacity and cognitive competencies.
- Gender: Girls tend to be more resilient than boys.
- Easy temperament.
- Favorable genes.
- Advantaged socioeconomic condition.
3. Community Factors:
- Supportive extended family unit fellow member engagement.
- A supportive relationship with a mentor.
- Positive schoolhouse experiences.
- Rubber neighborhood.
- Close community.
- Social support.
- Part of religious or religion community.
- Extracurricular activities.

4 Scientific discipline-Backed Strategies to Build Resilience In Children
Given this understanding of protective factors, nosotros can class specific strategies to help build it in our children.
While some of these factors can't be inverse, like the genetic makeup of each kid or their sex, there are many more of them that nosotros can actively provide or support.
Here are four proven strategies for raising resilient kids:
1. Warm, Responsive, Supportive Parenting is The All-time Fashion
The single most common cistron in building resilience is having at least one close, positive human relationship with a warm, responsive, and supportive parent or another adult caretaker.
Plus, when parents build a positive parent-child relationship, they can teach and instill in them many further protective factors.
Parents can build strong relationships through what child development experts call authoritative parenting. This parenting mode is characterized past high responsiveness coupled with loftier expectations.
Authoritative parents are warm and responsive to their children'south emotions, facilitating the development of emotional regulation, a key protective factor. They also permit autonomy and encourage independence, helping their children gain a sense of control of their own lives – another significant factor.
Authoritative parenting also encourages other valuable factors similar self-esteem, social competence, and communication skills.
Tough dear parenting, in contrast, does not support these protective factors and is less likely to produce strongly resilient kids.

2. Teach Problem-Solving and Coping Skills
Straight didactics coping skills can aid enhance resilient children.
Coping mechanisms are non only useful for dealing with severe hardship – just they're too helpful for handling everyday challenges and transitions. Then parents can treat ordinary changes or difficult times as opportunities to instill these skills.
In addition, through learning to cope with changes in their everyday lives positively, children can build a sense of self-efficacy and perceived control that will carry them through future challenges.
Positive coping skills include:
- Problem-solving
- Ability to brand realistic plans
- Positive reappraisal of stressful situations
- Volunteering
- Regular practice
- Extracurricular activities and grouping activities

3. Piece of work Towards a Healthy, Stable Environs
Parents can also help their children become resilient by working to ensure they have a positive home, school, and social environments.
Seeking assistance for any mental health or marital bug, finding ways to get more than resilient ourselves, and modeling coping strategies are all ways parents can improve our home environment.
At the same fourth dimension, parents can get involved in their children's schooling and work with teachers to ensure a positive schoolhouse feel.
And, finally, they can back up their children in developing positive social networks, as well as keep them away from peers who exert a harmful influence.
4. Don't Sweat the Small Stuff
Strive to create a positive and good for you environment for our children, but don't keep them in a bubble.
Nosotros tin can't maintain a perfect home, or protect our children from all possible schoolhouse and social stressors.
And the skilful news is that we don't need to.
That's because not all stress is harmful to children. In fact, children demand stress to build up tolerance. Gradual exposure to stressful times – at manageable levels – can actually help them develop coping strategies to get resilient. Psychologists telephone call this eustress or positive stress because it tin promote growth in coping skills.
But there's one primal caveat: The assist of a supportive developed is critical in managing stress and thereby turning stress exposure into resilience builder.

Resilience Theory: It's a Procedure
Stories abound of immature people who've overcome great arduousness or recovered from horrific experiences, but to thrive and prosper.
It would be easy to imagine that it takes something extraordinary to thrive confronting the odds. But in reality, what we demand to develop resilience is every bit unproblematic and ordinary as everyday connections and back up.
Resilience expert, Ann Masten, has found that resilience, far from being exceptional, is really quite common. She called this the "ordinary magic" vi .
Human being brains are malleable. This malleability or "plasticity" is greatest in early babyhood. So the before we start strengthening our children's capacity to resist stress, the better. Although possible, it'southward much harder to rewire our brains as we grow older.
Information technology's important to remember that the healthy development of resilience is an ongoing process, not a fixed point or end goal 7 .
From Resilience Theory, the conceptual framework psychologists utilise to sympathize how resilience works, nosotros know that information technology fluctuates over time and circumstances. A child may struggle in i domain but adapt well in another. The child may also be more or less resilient at unlike points in fourth dimension ii,8 .
Terminal Thoughts on Resilience in Children
Strengthening the protective factors to help children build resilience is a procedure. Parents play a big function in helping our children learn to adapt to whatever'south coming their fashion so they will yet thrive in the face up of arduousness.
References
-
1.
Zimmerman MA. Resiliency Theory. Wellness Educ Behav. July 2013:381-383. doi:10.1177/1090198113493782
-
2.
MASTEN AS, OBRADOVIC J. Competence and Resilience in Development. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. December 2006:xiii-27. doi:ten.1196/annals.1376.003
-
3.
Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ. Resilience to Babyhood Adversity: Results of a 21-Yr Report. In: Luthar SS, ed. Resilience and Vulnerability. Cambridge University Press; :130-155. doi:x.1017/cbo9780511615788.008
-
iv.
Masten A, Barnes A. Resilience in Children: Developmental Perspectives. Children. July 2018:98. doi:ten.3390/children5070098
-
5.
Kumpfer KL. Factors and Processes Contributing to Resilience. In: Longitudinal Research in the Social and Behavioral Sciences: An Interdisciplinary Series. Kluwer Academic Publishers; :179-224. doi:10.1007/0-306-47167-1_9
-
half-dozen.
Masten AS. Ordinary magic: Resilience processes in development. American Psychologist. 2001:227-238. doi:10.1037/0003-066x.56.3.227
-
7.
Fletcher D, Sarkar M. Psychological Resilience. European Psychologist. Jan 2013:12-23. doi:x.1027/1016-9040/a000124
-
8.
Masten Equally. Global Perspectives on Resilience in Children and Youth. Child Dev. December 2013:6-20. doi:10.1111/cdev.12205
Quizlet What Are Parents Of Children Who Develop Learning Goals Likely To Do?,
Source: https://www.parentingforbrain.com/resilience/
Posted by: garrettnectur.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Quizlet What Are Parents Of Children Who Develop Learning Goals Likely To Do?"
Post a Comment